Vermeiden Sie, dass Ihre Anfrage verspätet beantwortet wird, geben Sie bitte Ihre WhatsApp/Skype-Nachricht mit an, damit wir Sie sofort kontaktieren können.
Wir werden Ihnen innerhalb von 24 Stunden antworten. Wenn für dringenden Fall, fügen Sie bitte WhatsApp/WeChat: +86-13678899682 direkt.
Noisy streets, echoey rooms, and thin walls drain focus. The noise level creeps up; unerwünschtes Rauschen leaks through Wände und Decken and the Decke above. The fix is simple: combine Geräuschabschirmung, insulation, and smart build details to block, absorb, and dämpfen. vibrations—quiet you can feel.
Sound isolation stops noise from passing through structures; schalldicht insulation improves blocking by adding mass and Absorption. For a Decke or wall, use multiple layers von Trockenbau, a damping compound (like green glue), dense wool insulationund decouple the surfaces. This combo reduces Schallübertragung, raises stc, and delivers real db cuts.
Sound isolation bedeutet Anhalten sound transfer from one space to another, mainly by adding mass, decouple-ing surfaces, and controlling vibration. Schalldicht work targets the full path—airborne leaks, conduction through framing, and panel resonance. In simple terms: block, separate, and calm the shake.
Many people reach first for Schaumstoff. It helps inside a room because it improves Absorption and makes a space less reverberant, but isolation is different. In small amounts, foam will significantly improve echoes, not blocking. To truly reduce sound transmission, you need mass, sealed edges, and smarter construction—not Akustikschaum alone.
For tuned wall treatments that control reflections while you build isolation into the assembly, see our Akustikplatten aus Polyesterfasern.

What is sound isolation
A wall or Decke is a system: outer sheathing, Trockenbau, studs, cavity fill, and finish. Noise moves as pressure (airborne) and as structure-borne conduction. Wenn sound waves hit a surface, part reflects, part turns to heat (via Schallabsorption inside the cell structure of materials), and part passes through.
To block better, assemblies rely on adding mass (thicker boards), strategic decouple (channels or staggered stud), and viscoelastic sound damping layers. Inside the cavity, dense wool insulation oder Fiberglas helps attenuate mid-band frequency range energy. Together these steps lift stc performance and yield tangible db und db reduction benefits in daily use.
Explore dense PET felt schallabsorbierende Platten for the finish layer to calm room echoes after isolation is in place: schallabsorbierende Platten.
Every panel has a resonance point where it loves to vibrieren. Large, light boards ring; double layers shift that resonance downward while damping keeps peaks tame. If a Wand oder Decke shares studs, vibration passes easily—this is why people experience soundproofing problems even after adding layers.
Solutions that reduce resonance combine damping compound between boards (e.g., green glue), decouple with resilient channels, and keep edges sealed. Think of energy as Schallenergie: if it can’t couple cleanly, it dies out. Our wood veneer wall panels can finish an isolated assembly with warmth while preserving control: wood veneer wall panels.
stc (Sound Transmission Class) predicts speech blocking between typical rooms. Remember, decibel scales are logarithmic: +10 db sounds roughly twice as loud to many listeners. A standard interior partition (single Trockenbau each side, light fill) might score in the low 30s; upgraded builds push into the 50s+.
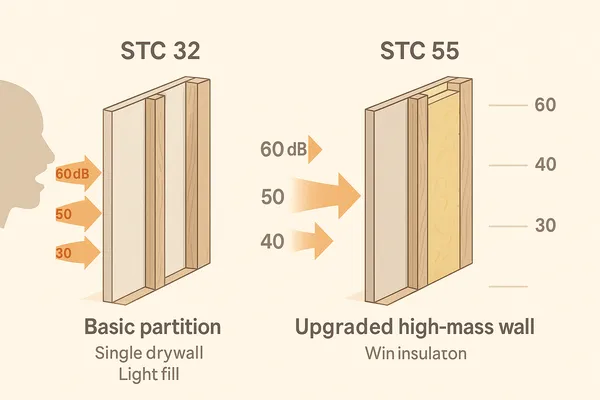
What is STC and how many dB do you need
Table: Typical Assemblies and Expected Sound Reduction
| Assembly (simplified) | Approx. STC | Notes on Geräuschminderung |
| Single 1× Trockenbau, no fill | ~33 | Light mass, weak isolation |
| Double Trockenbau + wool insulation | ~45–50 | Better blocking and Absorption |
| Double Trockenbau + green glue + dense fill | ~52–58 | Adds damping compound |
| Decoupled (channel) + mass + dense fill | ~55–63+ | Strong isolation |
When planning offices, studios, or classrooms, aim for assemblies that meet your target levels of noise. For spaces like an auditorium, isolation needs rise along with internal Akustik goals.
For packaged, project-ready finish options after isolation, see Holzlamellen-Wandplatten.
Decouple means breaking the rigid path so vibrations don’t pass straight through. Methods include resilient channels, clips, or staggered stud walls. With channels, where the drywall is attached matters: screws must hit the channel, not the stud, to keep the air space floating.
Add viscoelastic layers between multiple layers of board to den Klang dämpfen further. If budget allows, a “room within a room” (full framing separation) is the gold standard. After structure, finishing with tuned PET or wood treatments helps den Klang verbessern inside the space: try PVC-Lärmschutzplatten for durable, wipe-clean finishes.

How to decouple a wall or ceiling for better noise isolation?
mlv (mass loaded vinyl) is a flexible Schallmauer sheet. It adds mass where board layers are constrained by Dicke or weight. Mineral or Fiberglas batts and dense wool insulation excel as absorption material inside cavities. Rigid melamine sheets help with finish Absorption.
What about foams? Akustikschaum (often Offenzellig) helps in-room echo control, not blocking; open cell types breathe, Offenzellig designs trade mass for Absorption. Another Akustikschaum variant can help higher bands, but for niedrige Frequenz problems, mass and decouple dominate. Use foams as treatments, not primary blockers.
See PET felt finishes that pair well with isolated walls: PET-Filzplatten. For slatted diffusion plus Absorption, explore the Akustiklamellenplatte.
Downward thumps—impact noise—travel through structure. To calm footfall, float the subfloor or topping on pads (cork, rubber, neoprene), add underlay, or isolate the joist interface. Even a thin, properly chosen underlayment can dämpfen. the energy that tries to jump across the structure.
Where you can’t rebuild, add ceiling-side isolation below: clips + channel + mass. Tie-ins at beams and the second joist layer are critical. Finishes like slat wood can soften the reverberant character of large rooms; try Schalldämmplatten aus Holz when you also want a tactile timber look.
Panels and foams serve different roles. Use Akustikplatten (fabric-wrapped PET, wood slats with felt backing) to tune reflections and speech clarity; they’re schallschluckend finishes that make rooms feel calmer. Foams can be helpful for early reflections but aren’t your main blocker.
For finish choices that suit modern interiors and building materials schedules, browse Holzlamellen-Wandplatten again for diffusion-plus-Absorption, or pick verwendete Materialien in offices and studios such as Polyester-Akustikplatte alternatives when you need lighter, easy-to-install surfaces.
Isolation leaks at edges, outlets, and seams. Use acoustic caulk around board perimeters and a putty pad at boxes. Aim for airtight continuity: if air leaks, airborne noise leaks. Choose smart building materials, mind Dicke, and confirm every seam is sealed.
Where trims meet the Decke oder floor, keep breaks continuous. Be mindful of wood framing bridges. A tiny gap undone can undo a lot of noise isolation. Finish with a washable, decorative PET face where needed—see noise reduction panels.
Quote: “Design for the path the sound wants to take, and it won’t arrive.”
Example target: For a conference room beside an adjacent room, aim for a wall assembly delivering stc 55+. That typically means double board, green glue between, dense fill, and channel decouple. Expect clear speech privacy and measurable Rauschunterdrückung in day-to-day use.
Simple Before/After Table
| Metrisch | Before | After |
| Average speech spill (A-weighted) | 48 db | 34 db |
| Subjective privacy | Poor | Gut |
| Reported distraction | Hoch | Niedrig |
Finish layers that match design briefs: Holzlamellen-Wandplatten or PET-based schallabsorbierende Platten.
A Decke often needs clips + channel + double board. Keep services in the plenum, preserve air space, and avoid rigid backers touching the isolated shell. When fixtures must mount, use isolation grommets.
If you’re unsure, a reputable soundproofing company or our engineering team can propose schalldämmende Lösungen using PET and wood finishes that match your brand palette—without sacrificing performance. For design-led options, explore Holzlamellen-Wandplatten one more time for continuity across ceilings.
Isolation adds like resistors in series, and conduction loves shortcuts. One missed seam or rigid backer can bypass the best layers. Remember that Schallübertragung paths add up, and STC ignores niedrige Frequenz rumbles; doors, glazing, and ducts need equal care.
Wenn Sie insulate cavities, pick density that fits the assembly. Visco layers help across a wide frequency rangeund Schallmauer sheets can help when mass is limited. Pick finishes that are used for sound control and visual warmth—see custom PET and wood options on our site for coordinated packages.
Is “more foam” enough to soundproof a room?
Nein. Foam treats internal echo but not isolation. Use mass, decouple, and sealed layers; then add treatments to polish in-room akustisch quality.
Will panels fix traffic noise from outside?
Treat the shell first: windows, doors, and wall mass. Then add tuned finishes like PET felt to address traffic noise reflections.
What if I can’t rebuild the wall?
Add a new Trockenbau layer on channels with a damping compound, seal with caulk, and finish with decorative PET. It’s a fast retrofit.
Do I need special expertise to choose finishes?
We’re a manufacturer of PET and wood solutions for B2B teams. We help architects and contractors match finish, performance, and budget—globally.
How do I handle tricky ceilings with services?
Use clips, channels, and maintain air space. Route services through independent hangers; avoid rigid ties into the isolated shell.
As a China-based manufacturer of PET and wood acoustic finishes, we support distributors, designers, and contractors with OEM/ODM deliverables. We coordinate isolation-first builds and provide finish packages that meet specs and timelines. From small offices to large public builds, we help teams schalldicht without losing design intent.
Block: Use mass, multiple layers, and sealed edges.
Break: Decouple with channels or clips; avoid rigid bridges.
Calm: hinzufügen Absorption inside cavities; finish with PET or wood slats.
Seal: Caulk every seam; pad boxes with putty.
Überprüfen: Review fixtures at the Decke und floor so nothing ties through.
Beenden: Choose finishes that den Klang verbessern inside the space and match the spec.
A tech client had “paper walls.” We designed a clip-and-channel shell, added dense fill, two boards with green glue, then finished with PET slats. Result: clearer speech privacy, better focus, and happier teams. We measured db cuts across speech bands matching the plan, and the akustisch finish lifted visual quality too.
Anmerkung: If you need coordinated finish packages for offices, hospitality, education, or public works, our team supports specs, samples, and fast global dispatch—quietly and reliably.